What is the overall connection between nutrition and mental health?
What you eat directly affects mental health. Conversely, your mental health affects what you eat.
This food-mood connection can be positive or negative. Your food choices can boost mood, energy, and overall mental health. Unfortunately, what and how we eat can also negatively impact mood, productivity, and concentration. It can also increase the risk of anxiety and depression.
Food is the cornerstone of your brain. In many ways, you are what you eat. Healthy food is necessary for the physical structure of brain tissue and the neurotransmitters that carry messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Without healthy food, this process simply cannot occur seamlessly.
What do different nutrients do for your brain?
Carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates in foods such as grains, starches, fruits and vegetables provide glucose, the brain’s preferred source of energy. Eating carbohydrates triggers the release of the hormone insulin, which helps blood sugar enter cells. When insulin levels are elevated, more of the amino acid tryptophan can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect neurotransmitters such as serotonin. Neurotransmitters are the body’s chemical messengers that nerve cells or neurons use to talk to each other.
Protein.
Proteins in foods such as meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, eggs and dairy products provide amino acids. These are the building blocks of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and histamine.
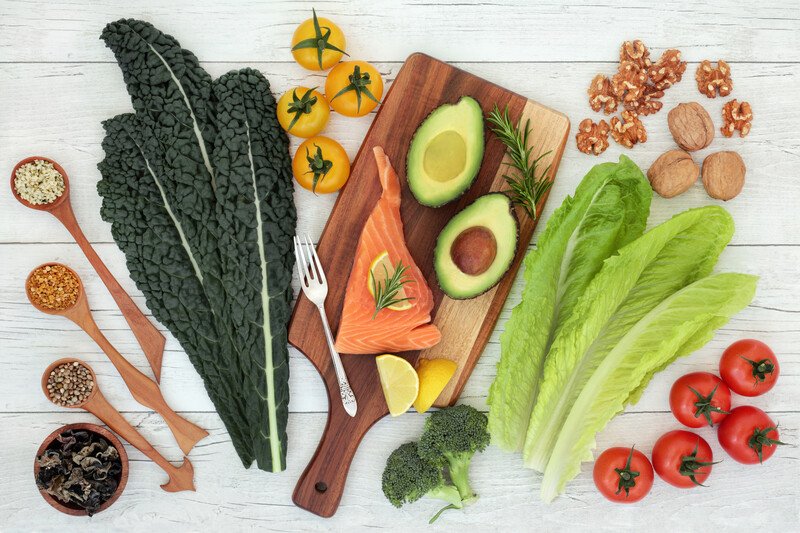

Fat
The fat in the brain mirrors the fat in the diet to some extent. About 35% of the brain and nervous system tissue is made up of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the omega-3 essential fatty acids known as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). ePA and DHA play important roles in brain development and signaling in brain cells.
Vitamins, Minerals, etc.
Minerals such as zinc, magnesium, selenium, copper, and iron, as well as B vitamins such as folic acid, vitamin B6, and B12 are nutrients commonly associated with mental health.
Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E and other bioactive components of plant foods such as flavanols, isoflavones and resveratrol have been linked to brain function. Most of these foods are available in a healthy diet that includes whole grains and plenty of fruits and vegetables (especially dark green leafy, orange vegetables).
Some studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to cognitive function and possibly depression.
Which foods are important for brain health and cognitive function?
The Mediterranean-style diet is not only good for physical health, but also for mental health and cognitive function. Aim for a diet rich in plant-based foods such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables. Include heart-healthy fats from fish, nuts, seeds, olive oil and legumes, lean meats, poultry and seafood as the foundation of your diet.
Studies have shown that diets that restrict the healthy foods mentioned above, as well as diets that consume large amounts of saturated fats, trans fats, or excess processed sugars can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, which can alter vascular function in the body. This may increase the risk of mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety and cognitive decline.
Please note that you do not need to eliminate any of these foods, the key is to be mindful of your choices. There is always room for fun and flexibility in our diets as well as foods like desserts and savory snacks that are chosen for taste and social enjoyment.


